
SMEs know and understand that they need to digitalize. The problem is that they lack expertise and services regarding digitalization often have a vague value proposition or approach the subject in a way that is often too abstract from the point of view of these companies.
Authors: Mariia Markova & Aki Vainio
Ketterät digistepit is a project funded by European Regional Development Fund and The Regional Council of Päijät-Häme and executed in cooperation between LAB University of Applied Sciences and LUT University with the aim of aiding SMEs of Päijät-Häme region to find ways to include digitalization in their strategies (LAB-ammattikorkeakoulu 2022). When working with these companies the approach selected is often to find ways to approach these subjects where the company can take concrete steps to reach concrete goals.
The ultimate goal of the project is to learn how these companies approach these subjects and how these universities can provide services for these companies in a way where the value proposition is interesting. The problem is that the organizational culture of these companies varies wildly, which means that one approach does not fit all, but in order to productize the activity, a clear model is needed.
Digitalization in SMEs
The fourth industrial revolution has dramatically impacted the need to adopt digital transformation (Saldanha 2019, 7-9). Digitalization has affected the whole competitive landscape, lowering the barriers to entry for the more digitally equipped companies and strengthening the rivalry and the threat of substitutes by disruptive solutions. Switching to digitally enabled services became easy, and the bargaining power of buyers has grown as never before. As a result, companies must leverage digital tools to meet customer requirements and expectations and maintain competitiveness. (Evans 2017.)
SMEs constitute the baseline of most European economies. They are an essential element of supply chains and provide a significant part of workplaces. (Bokša et al. 2020.) Particularly in Finland, SMEs provide 57% of workplaces. Moreover, in past years there has been a trend in the growth of self-employment, which resulted in 76.3% of Finnish SMEs being represented by micro-companies with less than ten employees. (OECD 2022.)
According to previous studies, there is a correlation between the size of the company and the pace of digital transformation. Thus, SMEs with less than 50 employees are adopting digitalization slower than more prominent companies. Therefore, they are more vulnerable and exposed to bankruptcy. (Strilets et al.2022.)
The challenges in SMEs’ adaptation to the new competitive landscape and leveraging digital tools are associated with the high diversity of backgrounds and attitudes to digitalization, the low level of skill diversity in companies, and the lack of technical competence. The SMEs mainly concentrate their financial and human resources on the main activity, leaving the digitalization process out of focus. (OECD 2017, 9; OECD 2021a.)
SMEs tend to experience difficulties taking the first steps toward digitalization and need more consistency and integrity. Yet most of the frameworks for digitalization do not address the gaps and challenges of SMEs, as SMEs are regarded as smaller versions of larger enterprises. Moreover, due to complicated formulations and professional vocabulary, digitalization guidelines are often perceived abstractly and do not encourage action. (Markova 2023.)
Design for the approach
Understanding the digitalization-related challenges SMEs face by consulting service providers enables the utilization of a design-thinking approach to digital consulting tailored for SMEs. Implementing simplified, comprehensive guidelines in digital consulting for SMEs can address the gaps associated with the need for skill diversity and technology understanding. In addition, it can improve SMEs’ digitalization-related decision-making processes, make the approach holistic, and enable sustainable results and opportunities for continuous improvement. The process is illustrated in Figure 1.
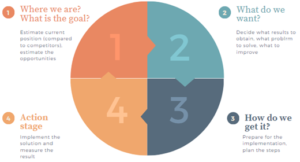
Figure 1. The illustration of digitalization guidelines for SMEs (Markova 2023, 35)
This approach is simple as SMEs often don’t have the opportunity to look at their enterprise architecture and develop it systematically. They need to prioritize the more acute shortcomings first. However, if no planning is done, this can lead to an impasse, where the company finds itself unable to integrate new systems and applications, because an existing key system has crucial limitations.
Maturity assessment is crucial in digitalization approaches for companies not planning to make disruptive changes. Defining the desired result of digital tool implementation is essential. Companies can choose tools to optimize internal or external processes, use data analytics, or improve customer experience. Customer needs, expectations, and goals should be considered, and digital tools can provide valuable information about customers. The implementation stage should include measuring results and comparing them to the plans. Therefore, companies should track the need for further improvements to stay competitive. An iterative approach may be taken if multiple problems are identified, and different tools may be implemented sequentially. (Markova 2023.)
References
Bokša, M., Šaroch, S., & Bokšová, J. 2020. Digitalization of SMEs. International advances in economic research, 2020 26.2, 175–177. Cited 6 Jun 2023. Available at https://lut.primo.exlibrisgroup.com/permalink/358FIN_LUT/vvk1gv/cdi_proquest_journals_2418452464
Evans N.D. 2017. Mastering digital business. E-book. BCS, The Chartered Institute for IT. Cited 10 Mar 2023. Available at https://learning.oreilly.com/library/view/mastering-digital-business/9781780173450/
LAB University of Applied Sciences. 2022. Ketterät digistepit. Cited 6 Jun 2023. Availabale at https://lab.fi/en/project/ketterat-digistepit
Markova, M. 2023. Digitalization in Finnish Technology Non-Native SMEs. Guidelines for SMEs in digital consulting provided by the DigiStep project. Bachelor’s thesis. LAB University of Applied Sciences, Faculty of Business and Hospitality Management. Cited 6 Jun 2023. Available at: https://urn.fi/URN:NBN:fi:amk-2023052915160
OECD. 2017. Enhancing the Contributions of SMEs in a Global and Digitalized Economy. Cited 25 Feb 2023. Available at https://www.oecd.org/industry/C-MIN-2017-8-EN.pdf
OECD. 2021. The Digital Transformation of SMEs, OECD Studies on SMEs and Entrepreneurship. OECD Publishing. Paris. Cited 2 Feb 2023. Available at https://doi.org/10.1787/bdb9256a-en
OECD. 2022. Financing SMEs and Entrepreneurs 2022: An OECD Scoreboard. OECD Publishing. Paris. Cited 23 Jan 2023. Available at https://doi.org/10.1787/e9073a0f-en
Saldanha, T. 2019. Why Digital Transformations Fail: The Surprising Disciplines of How to Take Off and Stay Ahead. E-book. Berrett-Koehler Publishers. Oakland. Cited 6 Jun 2023. Available at https://lut.primo.exlibrisgroup.com/discovery/fulldisplay?docid=alma991966398806254&context=L&vid=358FIN_LUT:LAB&lang=en&search_scope=LAB_CAMPUS_CDI&adaptor=Local%20Search%20Engine&tab=Everything&query=any,contains,why%20transformations%20fail&offset=0
Strilets, V., Frolov, S., Datsenko, V., Tymoshenko O. & Yatsko M. 2022. State support for the digitalization of SMEs in European countries. Problems and Perspectives in Management, Vol. 20 (4), 290-305. Cited 6 Jun 2023. Available at http://dx.doi.org/10.21511/ppm.20(4).2022.22
Authors
Mariia Markova is a student of business information technology at LAB University of Applied Sciences.
Aki Vainio is a senior lecturer of information technology at LAB university of Applied Sciences, who also acts as an expert in various projects regarding digitalization.
Illustration: https://pxhere.com/en/photo/758989 (CC0)
Published 6.6.2023
Reference to this article
Markova, M. & Vainio, A. 2023. Approaching the Digitalization of SMEs with Understanding. LAB Pro. Cited and date of citation. Available at https://www.labopen.fi/lab-pro/approaching-the-digitalization-of-smes-with-understanding/






