It is often challenging to succeed in business if you are entirely acting alone, without any partners or dynamic team. Successful collaboration with rapport forms a relationship where all parties feel empowered, engaged, and receive benefits. Furthermore, partnerships can support business growth in many ways. We have seen customer expectations changing rapidly in recent years, but how could SMEs respond to these changes and adapt their strategy? Perhaps by focusing on its current customers and designing a loyalty management strategy. Moreover, they might need other stakeholders to co-create when implementing that strategy.
Authors: Toni Räsänen & Brett Fifield
Customer expectations are changing, and their loyalty too
Consumers are using more digital channels than ten years ago. If companies fail to offer a service or an experience to the consumers in different channels, they might move on to other companies (Accenture Strategy 2014.) New customer expectations, preferences, and behaviors are normalizing (Bond Brand Loyalty 2020). The consumer has expectations about a service, where she compares these expectations with her perceptions of the experience (Bolton 2016). Daffy (2019, 36-37) advised focusing on understanding which customers to attract and retain, what matters to most of them, and how you can get the absolute best on these.
Strategy creation inside the SMEs operations
SMEs, small and medium-sized businesses are an essential part of all economies, and worldwide, they account for 99% of all business (Simpson et al. 2011 ). Komulainen (2018, 55-57) stated that many SMEs concentrate on the strategy’s immediate action planning and leave new business development and preparation of new strategic initiatives on a minor role. Their focus is on the optimization of daily operations and mitigation of risks. Lind (2012) emphasized that most SMEs have a resource-based approach, where their strategy is focused on optimizing their resources. Research by Huang and Brown (1999) highlighted that SMEs face the most significant challenges with sales and marketing and limited resources, e.g., cash, few customers, and focused mostly on current performance than the strategical part. (Simpson et al. 2011.)
And how to create a loyalty management strategy for SMEs?
A recent study by Räsänen (2020) focused on developing business growth for SMEs through loyalty management collaboration indicated that often small businesses have similar challenges on marketing, digitalization, strategy creation, and business operations. His mixed-method research indicated in figure 1 that SMEs requested support from the loyalty management supplier categorized in main themes; collaboration, interaction, support, and training. These ingredients highlight the foundation of the partnership, and with co-creation, e.g., in marketing, more profound loyalty engagement can be created.
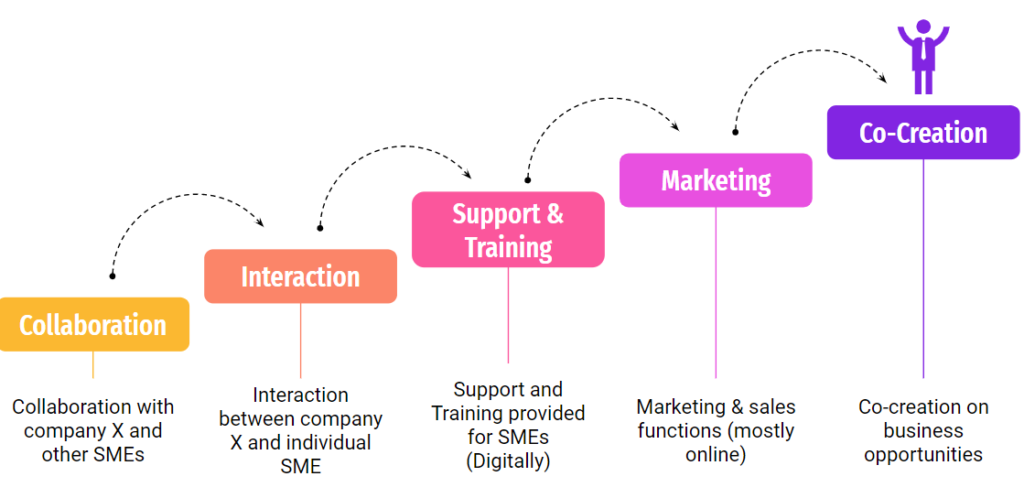
Figure 1. Main themes of the research process findings (Räsänen 2020).
When designing a successful loyalty program, companies need to define success measurements. They need to target the right consumers and determine what they want to achieve from them. These need to be consistent with the company’s overall strategy and brand messaging. (Huang & O’Toole 2020.) The well-aligned organization will focus on achieving the same outcomes and therefore pulling in the same direction. There needs to be a purpose, vision, or mission with a vivid description, meaning that everyone understands what is required to do (Daffy 2019, 171-173.)
Loyalty is about creating value-based, preferred relationships, where companies must focus on customer experience, relevance to them, and connect emotionally with their customers. Only after these actions can companies form a reliable loyalty program and strengthen their brand while continually learning more about their customer, motivation, and delivery through mass customization and not through mass communication (Pearson 2006.)
After the loyalty management strategy is set and educated in the entire organization, it is time to segment the value proposition to loyal customers. Creating loyalty is a process and needs involvement, interaction, and co-creation with several stakeholders, especially with the customers.
Collaboration, interaction and co-creation
According to Fuller & Kapoor (2014), co-creation is a collaborative process between an organization and its customers, staff, and other stakeholders, creating mutual value. Bolton (2016) stated that business success is founded on co-creation: creating service experiences that build the customer’s relationship with the organization. Ramaswamy & Ozcan (2014, 219-221 ) stated that companies should first apply the co-creation internally and, after developing and testing it, invite customers and other stakeholders to join.
Räsänen (2020) identified co-creation as the path to improve engagement and interaction during his research process. Furthermore, Räsänen identified valuable insights for the loyalty management program supplier by creating guidance, education, and partner management interaction for the SMEs. Partnering SMEs embraced new frameworks to implement loyalty management strategies with advice to become more digitally enhanced. Co-creation added value to the research participants, and two marketing campaigns were co-created and piloted. Several recommendations were created during the research process, which can be seen in figure 2.
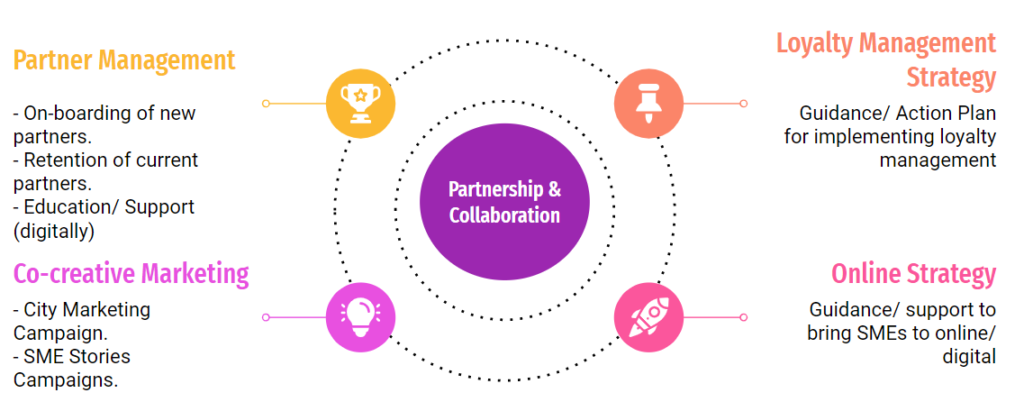
Figure 2. Recommendation projects on building loyalty management collaboratively (Räsänen 2020).
Co-creating added value to everyone
During the marketing co-creation, the researched partners received valuable insights on mutual goals. In the end, it is about the end-users; consumers. With improvements in customer journeys and developing their experience, an added value is being created for all parties. The objective was to collaborate and co-create by offering customized value propositions for customers, creating engagement through loyalty. These co-creation take-aways and research findings will be further developed for the loyalty management supplier and applied internationally.
Customer experiences build strong relationships between an organization and its customers, creating customer loyalty and switching costs, which (in turn) makes the organization more effective and efficient (Bolton 2016).
Building engagement together
Companies, who can utilize best their partners’ competencies and strengths, will succeed in the future. Co-operating skills and networking expertise become the core competencies of all partners in a way or another (Hakanen et al. 2007). Additional or missing competence can be achieved by networking with other companies. This enables the company to grow and scale faster as the networks can create action and capability planning and respond more quickly than completing these internally (Komulainen 2018;144.)
Räsänen (2020) stated that when this collaboration, interaction, and co-creation themes adhere together, a strengthened partnership can be established. All these actions build a more substantial knowledge base and competencies. Designing innovative products, services, or business models requires co-creation.
Customers should be at the core of the company’s strategy and building engagement and relationships with them. Loyalty management can be applied independently; however, collaborating with a partner might ensure the right direction. Furthermore, when consumers are included in the co-creation, more robust engagement can be achieved. These can lead to business growth with loyalty management; collaboratively together.
References
Accenture Strategy. 2014. Customer 2020: Are you future-ready or reliving the past? [Cited 11 Oct 2020]. Available at: https://www.accenture.com/_acnmedia/accenture/conversion-assets/dotcom/documents/global/pdf/dualpub_6/accenture-customer-2020-future-ready-reliving-past.pdfla=es-es
Bolton, R. 2016. Service Excellence: creating customer experiences that build relationships. Business Expert press. [Cited 15 Sept 2020]. Available at: https://ebookcentral.proquest.com/lib/lab-ebooks/detail.action?docID=4508881&query=Service+excellence+creating+customer+experiences
Bond Brand Loyalty. 2020. The Loyalty Report 2020, State of Loyalty. [Cited 7 Sept 2020]. Available at: https://info.bondbrandloyalty.com/tlr-2020
Daffy, C. 2019. Creating Customer Loyalty. Build lasting loyalty using customer experience management. London: Kogan Page.
Fuller, C. & Kapoor, A. The Definite Book of Branding. The Guide to Co-creation. Sage Publications. [Cited 29 July 2020]. Available at: https://ebookcentral.proquest.com/lib/lab-ebooks/reader.action?docID=1759064&ppg=321&query=the+guide+to+co-creation
Hakanen, M., Heinonen, U. & Sipilä. P. 2007. Verkostojen strategiat, menesty yhteistyössä. Helsinki: Edita.
Huang, X. & Brown, A. 1999. An analysis and classification of problems in small business’. International Small Business Journal. vol. 18, no.1, 73-85.
Huang, J. & O’Toole, T. 2020. McKinsey: Customer loyalty: The new generation. August 14, 2020 interview. [Cited 4 Oct 2020]. Available at: https://www.mckinsey.com/business-functions/marketing-and-sales/our-insights/customer-loyalty-the-new-generation#
Komulainen, V. 2018. Growth and Scaleup Enablers for SMEs. Helsinki: Books on Demand. [Cited 11 Oct 2020]. Available at: https://www.nextory.fi/
Lind, P. 2012. Small Business Management in Cross-Cultural environments. [Cited 13 Sep 2020] Available at: https://ebookcentral.proquest.com/lib/lab-ebooks/detail.action?docID=958315&query=small+business+management+in+cross-cultural
Pearson, B. 2006. Life is a shopping cart: three keys to building brands and improving customer loyalty. [Cited 14 Sept 2020]. Available at: https://ebookcentral.proquest.com/lib/lab-ebooks/reader.action?docID=285518&ppg=18
Ramaswamy, V. & Ozcan, K. 2014. The Co-Creation Paradigm. Stanford University Press. [Cited 13 Sep 2020] Available at: https://ebookcentral.proquest.com/lib/lab-ebooks/reader.action?docID=1656998&ppg=24
Räsänen, T. 2020. Developing Business Growth for SMEs through Loyalty Management Collaboration. Master’s Thesis. LAB University of Applied Sciences, Faculty of Business and Hospitality Management. Lahti. [Cited 30 Nov 2020]. Available at: http://urn.fi/URN:NBN:fi:amk-2020120426153
Simpson, M., Taylor, N. & Padmore, J. 2011. Entrepreneurship Marketing: Principles and Practise of SME marketing. Milton: Routledge. [Cited 10 Sept 2020]. Available at: https://ebookcentral.proquest.com/lib/lab-ebooks/detail.action?docID=667933
Authors
Toni Räsänen is studying in the MBA, International Business Development program at LAB University of Applied Sciences.
Brett Fifield is a Principal Lecturer in International Business at LAB University of Applied Sciences.
Illustration: https://pxhere.com/fi/photo/722676 (CC0)
Published: 11.12.2020
Reference to this article
Räsänen, T. & Fifield, B. 2020. Engagement builds loyalty. LAB Pro. [Cited and date of citation]. Available at: https://www.labopen.fi/en/lab-pro/engagement-builds-loyalty/